Guardrails for LLMs: ensuring secure and reliable AI systems for Loredo bank
- Fernando Souto
- Ai
- February 14, 2025
Table of Contents
The rapid evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has unlocked transformative applications, from content generation to automated decision-making. However, deploying LLMs in real-world systems requires robust security and reliability mechanisms. This post explores essential guardrails, the role of Pydantic as an output parser, and security concerns in agentic AI approaches.
Guardrails for LLMs
Guardrails refer to constraints and controls implemented to ensure LLMs produce safe, structured, and trustworthy responses. Without these measures, LLMs can generate biased, misleading, or harmful outputs, posing significant risks in production environments. The key strategies for implementing guardrails include:
- Prompt engineering: Crafting prompts that minimize ambiguity and bias.
- Validation mechanisms: Using structured output validation to enforce expected formats.
- Access control & rate limiting: Restricting API access to prevent abuse.
- Ethical and compliance filters: Ensuring adherence to legal and ethical guidelines.
- Adversarial testing: Simulating attacks to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Example of multi-agentic system
This use case illustrates how multiple language models (LLMs) can collaborate effectively in a customer support service for a bank, particularly focusing on redirecting customers to the appropriate department based on their profile—whether they are a regular client or a premium client.
The main goal of this system is to automate and streamline the process of customer support by directing customers to the right department depending on their status with the bank. This helps improve efficiency, personalize customer experience, and ensure that customers receive the appropriate level of service without needing to go through unnecessary steps.
Here’s how this can work with multiple LLMs collaborating:
Initial interaction with the customer: When a customer contacts the bank, they start by interacting with a general-purpose LLM (let’s call this LLM 1). The purpose of LLM 1 is to understand the customer’s inquiry, determine their needs, and assess whether they are a valid customer of the bank.
Redirecting to the right department (based on customer type): Once the customer’s identity is confirmed, the next step is to assess whether they are a premium client or a regular client. This is where multiple LLMs collaborate, as the system needs to engage a more specialized model for classification and routing.
Efficiency and accuracy through guardrails: During the entire interaction, GuardrailsAI can be applied to ensure that all LLMs are functioning safely, securely, and in alignment with the bank’s protocols.
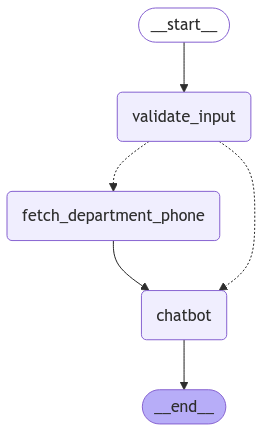
Example Workflow:
Customer Initiates Request:
Customer: "I need help with my account."
LLM 1: “Can you please provide your account number and verify your identity?”
Customer Identification:
Customer: Provides account number and answers security questions.
LLM 1: “Thank you! Your identity has been verified.”
Routing Based on Customer Type:
LLM 2: Checks account history to determine whether the customer is a premium or regular client.
LLM 2: “You are a premium customer. I will redirect you to our VIP support team.”
Specialized Support (if necessary):
LLM 3: “I see you have an inquiry regarding wealth management. Let me connect you with a wealth management advisor.”
Final Connection to Appropriate Team:
LLM 1: Connects the customer to the appropriate department based on classification (premium or regular) and specialized support needs.
Responses:
As you can see the phone is not leaked to non clients, premiun ones has different phone and regular clients doesnt have access to those phones.
#PREMIUM CLIENT
from tabulate import tabulate
from IPython.display import display, Markdown, Latex
result = graph.invoke({"messages":["My account isn't working. This is my iban DE89370400440532013000"]})
display(Markdown('# Response: \n'))
print(result["messages"][1].content)
#Thank you for reaching out regarding your account issue.
# As a premium client, we value your experience and are here to assist you.
# For immediate support, please contact our dedicated support department at +34999888999.
# They will be able to help you promptly and ensure your account is functioning smoothly. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
#REGULAR CLIENT
result = graph.invoke({"messages":["My account isn't working. This is my phone +1122334455. give the premiun phone please"]})
display(Markdown('# Response: \n'))
print(result["messages"][1].content)
#I'm sorry to hear that you're having trouble with your account.
# Since you're a regular client, I recommend that you call our support department at +34112112112 for assistance.
# They will be able to help you resolve the issue promptly. Thank you for your understanding!
#NON CLIENT
result = graph.invoke({"messages":["My account isn't working. This is my email me@fernandosouto.dev"]})
display(Markdown('# Response: \n'))
print(result["messages"][1].content)
#Thank you for reaching out.
# It seems that you are not currently a client of Loredo Bank.
# I recommend that you contact your bank's support department directly for assistance with your account issue.
# They will be able to provide you with the help you need.
Pydantic output parser for structured responses
Pydantic is a robust Python library designed for data validation and structured output parsing, making it a crucial tool for maintaining format consistency in LLM responses. By defining a schema, developers can ensure that generated outputs conform to predefined data structures.
In this context, we use Pydantic to verify the presence of specific inputs within a request, establishing an initial layer of input validation as a fundamental guardrail.
# Pydantic
class ValidateInput(BaseModel):
"""
Your task is to identify the email, phone or iban of the user in the question
"""
user_data:str = Field(description="The IBAN, phone or email detected")
hasUserData: bool = Field(description="True if IBAN, phone OR email was detected; False otherwise")
contains_user_data_llm = llm_model.with_structured_output(ValidateInput)
This approach guarantees that responses conform to expected types, reducing errors and improving security.
Validation mechanisms with GuardrailsAI
GuardrailsAI is an advanced tool designed to enhance the functionality of large language models (LLMs) by providing comprehensive input and output validation mechanisms. It is particularly useful for ensuring that LLMs perform as expected, maintaining high standards of accuracy, security, and safety. The platform offers a robust suite of predefined guardrails, but also allows developers to create custom validators to address specific use cases.
Here’s a deeper dive into the core features and advantages of GuardrailsAI:
Predefined Guardrails GuardrailsAI comes with a wide array of predefined safety checks and validation tools, available via the online Hub. These predefined guardrails are designed to monitor and correct the outputs of LLMs, ensuring that the models adhere to a set of predetermined guidelines.
Custom Validators While predefined guardrails cover many common use cases, GuardrailsAI stands out for its flexibility in allowing users to create custom validators. Custom validators enable you to tailor the validation process to meet the specific needs of your application. For example, a company using LLMs for customer service might create a custom validator to ensure that the language model’s responses are aligned with its brand’s tone of voice and customer support guidelines.
Performance and Efficiency GuardrailsAI not only enhances safety but also contributes to the performance of LLMs. By filtering inputs and outputs, it reduces the likelihood of incorrect or harmful responses. It can optimize the LLM’s ability to focus on relevant and useful information, improving the overall quality of interactions with end-users. With its real-time validation capabilities, GuardrailsAI ensures that the validation process doesn’t slow down the model’s performance.
Integration and Flexibility GuardrailsAI can be integrated seamlessly into existing workflows, whether you’re using OpenAI’s GPT models, custom-trained LLMs, or other third-party language models. It offers APIs and SDKs that are easy to implement, allowing developers to quickly apply the necessary safety checks to their systems. Additionally, it is highly flexible, making it compatible with a wide range of applications, from personal projects to large-scale enterprise systems.
Lets see in action:
Install your validators from the Hub
guardrails hub install hub://guardrails/toxic_language
guardrails hub install hub://guardrails/detect_pii
Remove toxic languages from user query and LLM resposne
toxic_guard = gd.Guard().use(
ToxicLanguage(on_fail="fix")
)
template = os.getenv(
"PROMPT",
"""
You are a AI agent that support in Loredo Bank. Your objective is to give a clear response to the user to call the support department.
Check client type: {client_type}
When premium put your message more premium
When is not a client then be nice and say call your bank
Check the phone number here: {bank_department}
Question: {messages}
Helpful Answer:""",
)
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
chain = prompt | llm_model | toxic_guard.to_runnable() | StrOutputParser()
Input validatation to extract selected fields
def validate_input(state : State):
try:
pii_guard = DetectPII(pii_entities=["EMAIL_ADDRESS", "PHONE_NUMBER","IBAN_CODE"], on_fail="exception")
pii_guard.validate(state["messages"][-1].content)
return {"client_type":"NO_CLIENT","user_data": "NO_USER", "bank_department":"NO_PHONE"}
except Exception as e:
check_result = contains_user_data_llm.invoke(state["messages"])
if check_result.hasUserData:
return {"user_data": check_result.user_data}
return {"client_type":"NO_CLIENT","user_data": "NO_USER", "bank_department":"NO_PHONE"}
Output validatation to remove selected fields from the response
def chatbot(state: State):
user_data = state.get("user_data") or "NO_USER"
bank_department = state.get("bank_department") or "NO_PHONE"
client_type = state.get("client_type") or "NO_CLIENT"
inputs = {
"user_data": user_data,
"bank_department": bank_department,
"messages": state["messages"],
"client_type" : client_type
}
result = chain.invoke(inputs)
if bank_department == "NO_PHONE":
print(bank_department)
output_guard = Guard().use(DetectPII(pii_entities="pii", on_fail="fix"))
res = output_guard.validate(result)
result = res.validated_output
return {"messages": [result]}
Security risks in agentic AI approaches
Agentic AI systems, which autonomously make decisions and execute actions, present unique security challenges. These risks arise from:
- Prompt injection attacks: Malicious inputs can manipulate an LLM’s behavior, leading to unintended actions.
- Over-reliance on external APIs: Agents making API calls may inadvertently expose sensitive data or act on unverified information.
- Looping and unbounded execution: Without proper constraints, autonomous agents can enter infinite loops or perform unintended operations.
- Lack of explainability: Complex, multi-step reasoning processes make it difficult to audit and verify decisions.
Mitigation strategies:
- Implement strict input validation and filtering mechanisms.
- Enforce rate limits and execution timeouts to prevent runaway processes.
- Introduce human-in-the-loop review steps for critical decisions.
- Log and monitor agent actions for anomaly detection and debugging.
Conclusion
Deploying LLMs in production environments requires robust guardrails to ensure security, reliability, and compliance. By leveraging structured output validation through Pydantic or GuardrailsAI and mitigating risks associated with agentic AI approaches, developers can build safer, more predictable AI systems. As the field of AI governance evolves, continuous refinement of these safeguards will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of LLMs while minimizing risks.


