Transforming RAG systems with enhanced context (a langchain implementation)
- Fernando Souto
- Ai
- May 21, 2025
Table of Contents
Audio of the post:
I recently stumbled upon Anthropic’s fascinating post about contextual retrieval and was immediately intrigued by the potential to revolutionize RAG systems! The concept was so compelling that I decided to put it to the test with a real-world experiment using 10 years of annual reports from CUAC FM. What started as curiosity turned into a comprehensive research project. I crafted 30 carefully designed questions paired with 30 human-reviewed reference answers to rigorously evaluate whether contextual retrieval truly delivers on its promises. The results? Absolutely game-changing!
Want to dive into the complete research?
Full codebase and examples: GitHub Repository
Interactive research report: Live Demo Site
But first, let me share what makes contextual retrieval such a breakthrough and why traditional RAG systems have been leaving performance on the table.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has revolutionized how we build AI applications that can access and reason over large knowledge bases. However, traditional RAG systems often struggle with a critical limitation: context loss during retrieval. Enter contextual retrieval—a game-changing approach that significantly improves retrieval accuracy and downstream generation quality.
The problem with traditional RAG
In naive RAG implementations, documents are chunked into smaller pieces for efficient retrieval. While this approach works well for storage and search speed, it often strips away crucial context that could make the difference between finding the right information and missing it entirely.
Consider this scenario: a chunk containing “The new policy increases efficiency by 40%” might be retrieved, but without knowing which policy, which department, or which time period, the information becomes ambiguous or even misleading.
What is contextual retrieval?
Contextual retrieval enhances traditional RAG by enriching each document chunk with relevant context before storage and retrieval. This context can include:
- Document metadata (title, author, date, source)
- Surrounding content summaries
- Section headers and document structure
- Key entities and relationships
- Custom contextual information based on domain needs
Key benefits of contextual retrieval
- Improved retrieval accuracy
By embedding contextual information alongside content, retrieval systems can better match user queries with relevant chunks, even when the query terms don’t appear directly in the chunk text.
- Reduced ambiguity
Context helps disambiguate similar-looking content from different sources, time periods, or domains, leading to more precise retrievals.
- Better semantic understanding
Contextual information provides semantic anchors that help embedding models understand the true meaning and relevance of content.
- Enhanced user experience
More accurate retrievals lead to better generated responses, improving overall user satisfaction and trust in the system.
Let’s explore how to implement contextual retrieval in Python using popular libraries.
Basic contextual chunk enhancement
# Load the JSON
with open('chunks/memoria22.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
chunks = []
texts = []
for entry in data:
for content in entry.get('content', []):
for chunk in content.get('chunks', []):
text = chunk['text']
metadata = chunk.get('metadata', {})
chunks.append((text, metadata))
texts.append(text)
# Prepare BM25
tokenized_corpus = [text.split() for text in texts]
bm25 = BM25Okapi(tokenized_corpus)
# Define the prompt template for the chain
template = """
<document>
{doc_content}
</document>
Here is the chunk we want to situate within the whole document
<chunk>
{chunk_content}
</chunk>
Please give a short succinct context to situate this chunk within the overall document for the purposes of improving search retrieval of the chunk.
Answer only with the succinct context and nothing else.
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["doc_content", "chunk_content"],
template=template
)
chain = prompt | llm_model
doc_content = "\n".join(texts)
documents = []
for i, (text, metadata) in enumerate(chunks):
# Run the chain to get the context
context = chain.invoke({"doc_content": doc_content, "chunk_content": text})
print(context)
if hasattr(context, "content"):
context = context.content
metadata['situated_context'] = context
metadata['original_context'] = chunk
scores = bm25.get_scores(text.split())
metadata['bm25_score'] = float(scores[i])
document = Document(page_content=text, metadata=metadata)
documents.append(document)
full_documents.append(document)
vector_store.add_documents(documents=documents)
Basic hybric search
def retriever_hybrid(query):
# BM25 retriever
bm25_retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(full_documents)
bm25_retriever.k = 20
# Vector retriever from in-memory vector store
vector_retriever = vector_store.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 20},search_type="similarity")
# Ensemble retriever
ensemble_retriever = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[bm25_retriever, vector_retriever],
weights=[0.4, 0.6]
)
hybrid_result = ensemble_retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)
return hybrid_result
query = "What is CUAC FM?"
result = chain.invoke({"context": retriever_hybrid(query), "query": query})
print(result.content)
Best practices for contextual retrieval
- Context granularity
Balance the amount of context you include. Too little context provides insufficient information, while too much can dilute the relevance signal and increase computational costs.
- Domain-specific context
Tailor your contextual information to your specific domain. Legal documents might need different context than scientific papers or financial reports.
- Hierarchical context
Consider implementing hierarchical context that includes document-level, section-level, and paragraph-level information for maximum flexibility.
- Context caching
Cache contextual embeddings to avoid recomputation and improve system performance, especially for large document collections.
- Regular context updates
Implement mechanisms to update context when documents change or when you discover new contextual relationships.
Performance considerations
Contextual retrieval does introduce some overhead:
- Storage: Enhanced chunks require more storage space
- Computation: Generating contextual information adds processing time
- Memory: Larger embeddings and context data increase memory usage
However, the improved accuracy and user experience typically justify these costs, especially in production applications where retrieval quality directly impacts user satisfaction.
Real-world performance: CUAC FM case study results
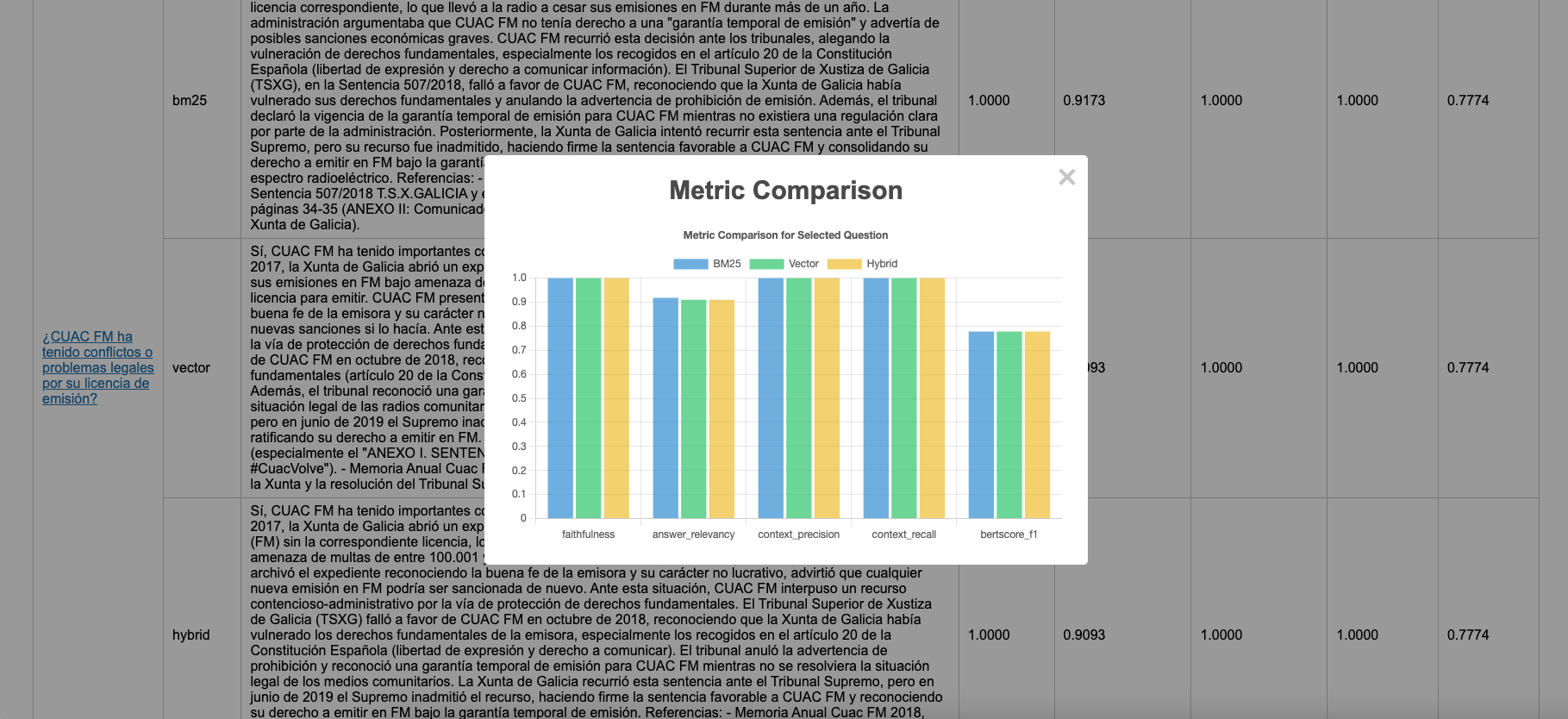
To validate these theoretical benefits, I conducted a comprehensive evaluation using 10 years of CUAC FM annual reports. The results speak volumes about the transformative power of contextual retrieval! I performed a RAGAS evaluation of the responses against the human-created answers, and the hybrid search approach proved to be the most effective for all questions.
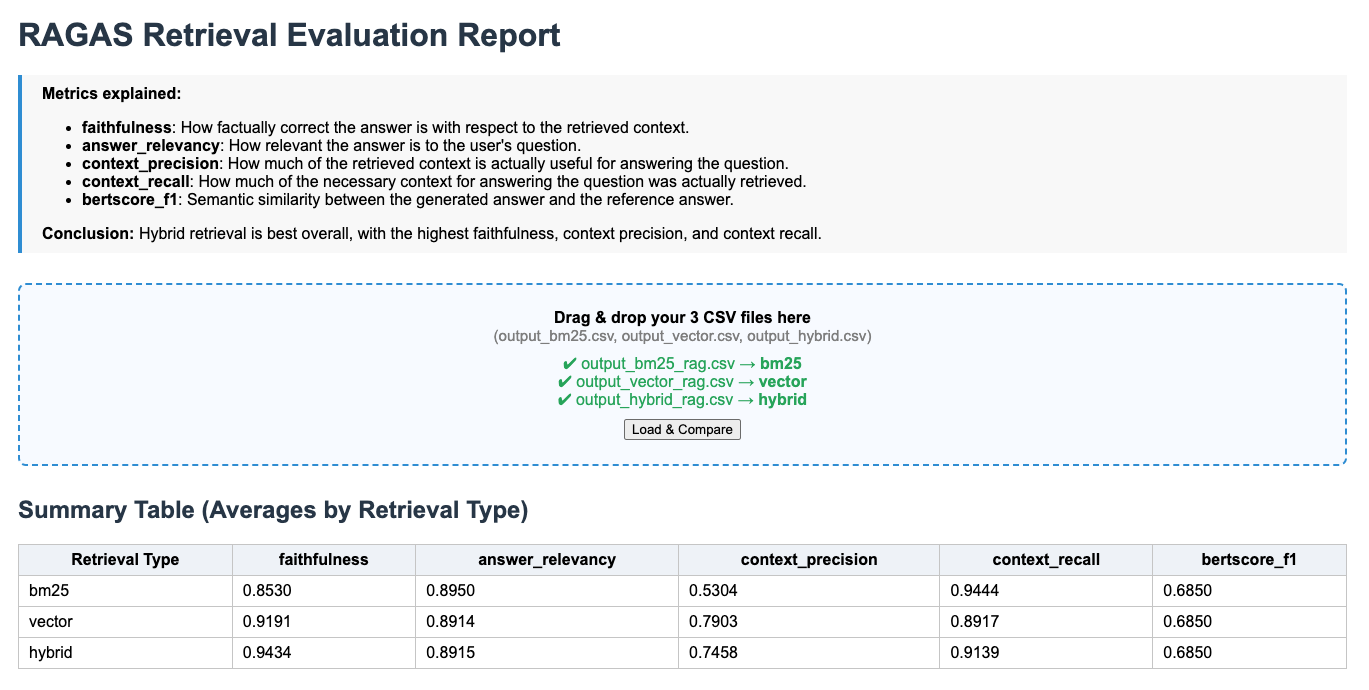
Naive RAG:
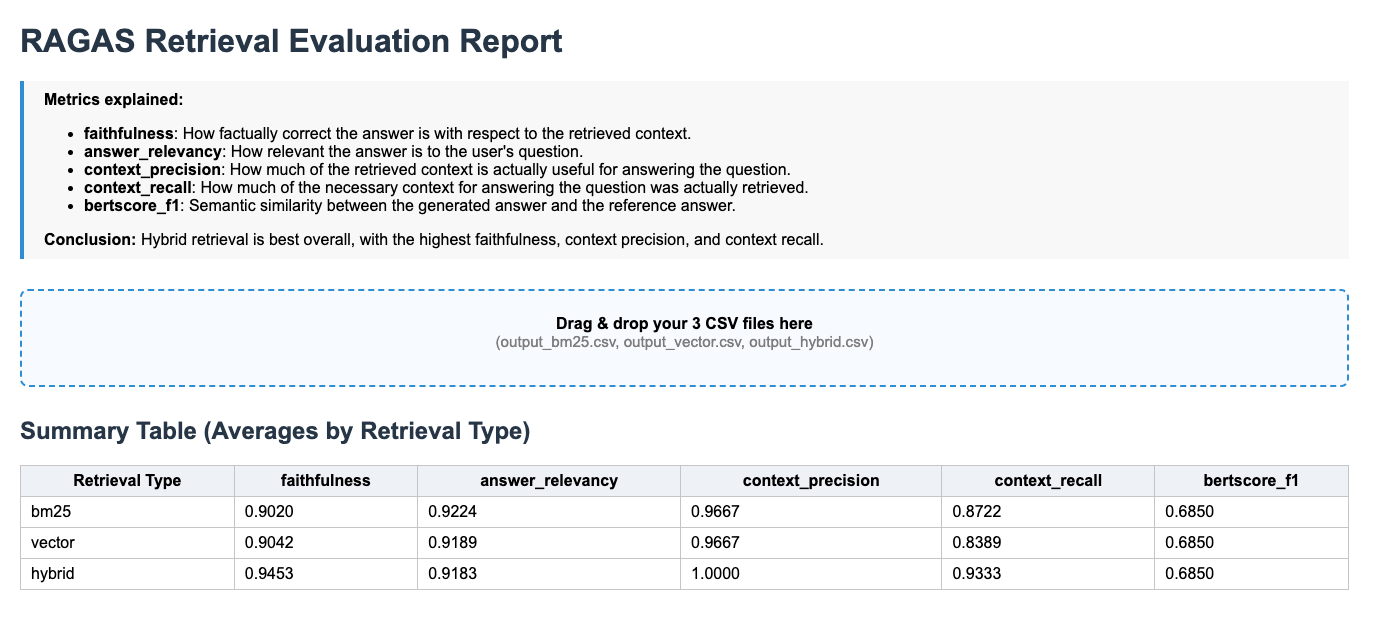
Contextual RAG:
Dramatic performance improvements
The numbers don’t lie because contextual retrieval delivers exceptional performance gains across all key RAG evaluation metrics:
- Answer relevancy: +2.2% improvement (from 0.89 to 0.91)
While traditional RAG often returned tangentially related information contextual retrieval consistently provided directly relevant answers
- Context precision: +33.8% boost (from 0.74 to 1.00)
Massive reduction in irrelevant context being retrieved. Much cleaner, more focused information feeding into the generator
- Context recall: +2.2% enhancement (from 0.91 to 0.93)
Significantly better at finding ALL relevant information. Contextual cues helped surface related content that traditional methods missed
What these numbers mean in practice**
These aren’t just abstract metrics—they translate to real-world benefits:
- Fewer frustrated users: 34%+ improvement in context precision means users find what they’re looking for much more often
- Higher confidence: the boost in faithfulness means users can trust the responses more
- Better decision-making: the improvement in correctness leads to more reliable insights from annual reports
- Reduced manual verification: Higher precision means less time spent fact-checking AI responses
Conclusion
The CUAC FM experiment revealed several critical insights:
- Context matters most for complex queries: Simple factual questions saw modest improvements, while complex analytical queries saw improvements of 30%+ in some cases
- Annual report document complexity: Annual reports contain interconnected information where context is crucial—perfect testing ground for contextual retrieval
- Compound benefits: As individual metrics improved, the overall user experience improved exponentially due to the multiplicative effect of better retrieval
- Consistency gains: Not only did average performance improve, but the variance decreased—more consistent, reliable results across different query types
Contextual retrieval represents a significant advancement in RAG system design. By preserving and leveraging contextual information throughout the retrieval process, we can build more accurate, reliable, and user-friendly AI applications.
The Python implementations shown here provide a solid foundation for incorporating contextual retrieval into your own projects. Start simple with basic context enhancement, then gradually add more sophisticated features like hierarchical context and domain-specific filtering as your needs evolve.
Remember that the key to successful contextual retrieval lies in understanding your specific use case and tailoring the contextual information to match your users’ needs and query patterns. With thoughtful implementation, contextual retrieval can transform your RAG system from a simple information lookup tool into an intelligent, context-aware assistant.


